[Leetcode] Flatten Nested List Iterator(Medium)
LeetCode 341 - Flatten Nested List Iterator
You are given a nested list of integers nestedList. Each element is either an integer or a list whose elements may also be integers or other lists. Implement an iterator to flatten it.
Implement the NestedIterator class:
NestedIterator(List<NestedInteger> nestedList)Initializes the iterator with the nested listnestedList.int next()Returns the next integer in the nested list.boolean hasNext()Returnstrueif there are still some integers in the nested list and false otherwise.
Your code will be tested with the following pseudocode:
initialize iterator with nestedList
res = []
while iterator.hasNext()
append iterator.next() to the end of res
return res
If res matches the expected flattened list, then your code will be judged as correct.
example
Input: nestedList = [[1,1],2,[1,1]]
Output: [1,1,2,1,1]
Explanation: By calling next repeatedly until hasNext returns false, the order of elements returned by next should be: [1,1,2,1,1].
Input: nestedList = [1,[4,[6]]]
Output: [1,4,6]
Explanation: By calling next repeatedly until hasNext returns false, the order of elements returned by next should be: [1,4,6].
How can we solve this problem?
這一題就是一題設計的題目,可以想象成是一個FileSystem,裡面可能存的是文件(Integer)或者是文件夾(List)。因此,我們可以發現他就是一顆Tree。所以,我們只要從左到右拿到Integer,並順序輸出即可。
如圖: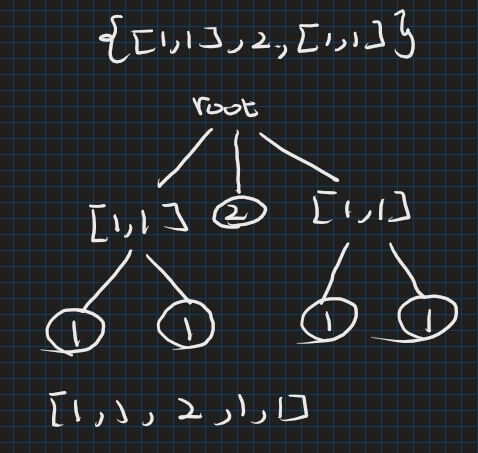
Solution(Recursion):
我們可以在initial透過Recursive Function來遍歷Input,並把所有Integer先Push到Array/List裡面。然後在定義一個pointer用於存取Next的值即可。
/**
* // This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists.
* // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
* class NestedInteger {
* public:
* // Return true if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list.
* bool isInteger() const;
*
* // Return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer
* // The result is undefined if this NestedInteger holds a nested list
* int getInteger() const;
*
* // Return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list
* // The result is undefined if this NestedInteger holds a single integer
* const vector<NestedInteger> &getList() const;
* };
*/
//calling hasNext -> next
class NestedIterator {
vector<int> ans;
// vector<NestedInteger> list;
int cur = 0;
void getValue(vector<NestedInteger>& data){
for(int i = 0;i<data.size();i++){
if(data[i].isInteger()) ans.push_back(data[i].getInteger());
else getValue(data[i].getList());
}
}
public:
NestedIterator(vector<NestedInteger> &nestedList) {
getValue(nestedList);
}
int next() {
return ans[cur++];
}
bool hasNext() {
return cur < ans.size() ? true:false;
}
};
/**
* Your NestedIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* NestedIterator i(nestedList);
* while (i.hasNext()) cout << i.next();
*/
Solution(Iteration):
這個解法是透過在Calling hasNext()的時候將當前container的最前面的那個element展開來(如果是一個list),並把展開來的element放到container最前面,從而確保來container的最前面的element是Integer,呼叫next()時,都會return Int。
/**
* // This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists.
* // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
* class NestedInteger {
* public:
* // Return true if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list.
* bool isInteger() const;
*
* // Return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer
* // The result is undefined if this NestedInteger holds a nested list
* int getInteger() const;
*
* // Return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list
* // The result is undefined if this NestedInteger holds a single integer
* const vector<NestedInteger> &getList() const;
* };
*/
//calling hasNext -> next
class NestedIterator {
// vector<int> ans;
vector<NestedInteger> list;
public:
NestedIterator(vector<NestedInteger> &nestedList) {
list = nestedList;
}
int next() {
//here we always return the first one
// cout << storage.size() << endl;
int res = storage.begin()->getInteger();
// cout << res <<endl;
storage.erase(storage.begin());
return res;
}
bool hasNext() {
//we check our storage here
//if the first elements is not a integer ,we try to get the interget from the list and append to our storage
while(!storage.empty() && !storage.front().isInteger()){
//get the first one from the storage
vector<NestedInteger> data = storage.front().getList();
storage.erase(storage.begin());
//append to the front of the storage that retrieved from the list
for(int i = data.size()-1;i>=0;i--)
storage.insert(storage.begin(),data[i]);
}
// if(storage.front().isInteger()) cout << storage.front().getInteger();
return !storage.empty();
}
};
/**
* Your NestedIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* NestedIterator i(nestedList);
* while (i.hasNext()) cout << i.next();
*/