[Leetcode] Shortest Unsorted Continuous Subarray(Medium)
LeetCode 581 - Shortest Unsorted Continuous Subarray
Given an integer array nums, you need to find one continuous subarray that if you only sort this subarray in ascending order, then the whole array will be sorted in ascending order.
Return the shortest such subarray and output its length.
example:
Input: nums = [2,6,4,8,10,9,15]
Output: 5
Explanation: You need to sort [6, 4, 8, 10, 9] in ascending order to make the whole array sorted in ascending order.
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4]
Output: 0
Input: nums = [1]
Output: 0
How can we solve this problem?
這題比較難懂一點點,這裡先做一下題目的解釋。這題主要先問的是在輸入的Array裡面找到一個最小需要排序的Sub-array。
從例子[2,6,4,8,10,9,15]中,我們可以很明顯的看到[6,4,8,10,9]並不是ascending order(順序),而這個sub-array要進行排序的話,所有elements都需要進行排序,所以,他的length是5。
再舉另外一個例子[1,3,2,3,3],這個Array我們可以看到[3,2,3,3]並不是順序的,但是在這個sub-array裡面,只有[3,2]需要排序,所以,他的結果會是2。
那我們應該要怎麼解呢?
一個最簡單的解法是定義一個額外的array,而這個array的element跟原來的一樣,但是已經被排序過的。因此,只要比較原本的array和排序過的array有幾個element的位置不一樣就知道結果了。但Time Complexity是是O(n log n) - 排序的時間,而Space Complexity則是O(n)
Solution:
vector<int> temp = nums;
sort(temp.begin(),temp.end()); //n log n
int start = nums.size() - 1;
int end = 0;
//finding the starting point which is not as same as the sorted array
//finding the ending print which is not as same as the sorted array
for(int i =0;i<nums.size();i++){
if(nums[i] != temp[i]){
start = min(i,start); //
end = max(end,i);
}
}
return end - start >= 0 ? end - start + 1 : 0;
另外一種解法是通過Two-pointer approach來解。我們先要找到左手邊有問題的地方的最小值(1,4,7,5,3,6 最小值為3)以及右手邊有問題的地方的最大值(1,4,7,5,3,6 最大值為7)。然後,要找出左手邊第一個被影響的index(nums[index] > 最小值)。同理也要找出右手邊第一個被影響的最index(nums[index] < 最大值)。這樣我們就能找出有問題的區間[left,right],在根據left,right得出最終結果。
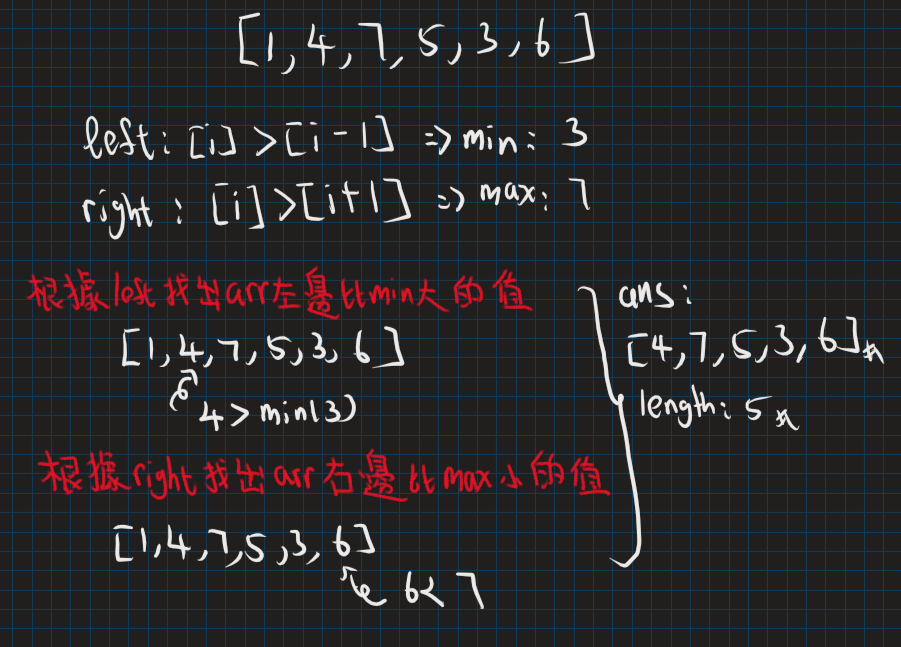
Solution:
解法二:
int start = INT_MAX;
int end = INT_MIN;
for(int i = 1;i<nums.size();i++){
if(nums[i] < nums[i-1]) start = min(nums[i],start);
}
for(int i = nums.size() - 2;i>=0;i--){
if(nums[i] > nums[i + 1]) end = max(nums[i],end);
}
int left,right;
//scanning the value from the left to the right that is less than maximum value
for(left = 0;left<nums.size();left++){
//finding the descending point
if(start < nums[left]) break;
}
//scanning the value from the right to the left that is less than minimum value
for(right = nums.size() - 1;right >= 0;right--){
if(end > nums[right]) break;
}
//we need to find out the right-most point
return right - left >= 0 ? right - left + 1 : 0;