[Leetcode] Short Encoding of Words(Medium)
820 - Short Encoding of Words
A valid encoding of an array of words is any reference string s and array of indices indices such that:
words.length==indices.length- The reference string
sends with the'#'character. - For each index indices[i], the substring of s starting from
indices[i]and up to (but not including) the next'#'character is equal towords[i].
Given an array of words, return the length of the shortest reference string s possible of any valid encoding of words.
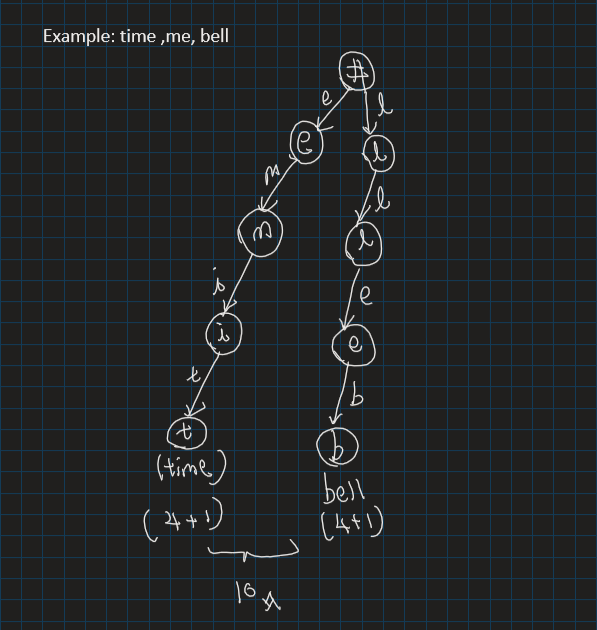
example:
Input: words = ["time", "me", "bell"]
Output: 10
Explanation: A valid encoding would be s = "time#bell#" and indices = [0, 2, 5].
words[0] = "time", the substring of s starting from indices[0] = 0 to the next '#' is underlined in "time#bell#"
words[1] = "me", the substring of s starting from indices[1] = 2 to the next '#' is underlined in "time#bell#"
words[2] = "bell", the substring of s starting from indices[2] = 5 to the next '#' is underlined in "time#bell#"
Input: words = ["t"]
Output: 2
Explanation: A valid encoding would be s = "t#" and indices = [0].
How can we solve this problem?
這題看上去好像很難理解它要我們解決什麼問題。但是我們可以從例子中可以觀察到他就只是單純用#來分隔每個子串。例如:time,me,bell會以這樣的方式進行Encoding,time#me#bell。但是問題要找出我們最短的是Encoding 長度為多少,也就是有重疊的Word我們無需額外加入到子串中,就剛才的例子我們可以看得出來time和me都包含了me。所以,我們Encoding會從time#me#bell縮短為time#bell#
哪我們要怎麼知道是否不用額外加入到字串中呢?
題目中有給出幾個條件(不符合條件需插入至String結尾):
- 對於任何
words[j],從string中的indices[i]到#前,與words[j]相同,也就是與words[j]是string的後綴(suffix)。例如:time和me,me是time的後綴。 words[i]的長度等於indices的長度。也就是words[i]-indices會等於words[j]。例如words[i]為4,indices為1,words[j]為2。4-1!=2,也就是代表words[j]不是words[i]的後綴。
Solution:
我們可以透過
Tire Tree
來解決這個問題。因為我們要知道words有沒有相同後綴(suffix),所以建構Tree的時候,需要放過來插入。直到 leaf(葉子) 就會知道當前有相同後綴(suffix)的長度為多少,最後加總加一起,就是我們要的結果。
class TrieNode{
public:
TrieNode(){
node = vector<TrieNode*>(26);
}
vector<TrieNode*> node;
};
int AddWord(TrieNode* root,string& w){
int res = -1; //if some words have the same suffix,it will return 0 ,-1+'#' = 0
for(auto i = w.rbegin();i<w.rend();i++){
if(!root->node[*i - 'a']){
root->node[*i - 'a'] = new TrieNode();
res = w.length();
}
root = root->node[*i - 'a'];
}
return res + 1; //extra
}
class Solution {
public:
int minimumLengthEncoding(vector<string>& words) {
int res = 0;
sort(words.begin(),words.end(),[&](string& a, string& b){
return a.length() > b.length();
});
TrieNode* root = new TrieNode();
for(int i = 0;i<words.size();i++)
res += AddWord(root,words[i]);
// findShortWords(0,root,res);
return res;
}
};
另外一種解法是我們只需要知道哪些words[j]跟words[i]有共同的suffix且符合條件。
- 過濾掉重複的
words,並生成unique的list - 大到小排序(根據字串的長度),因為我們要知道
words[i]是否包含了words[j]。如果words[i].length()<words[j].length()就一定不會包含。 - 計算長度:
- 看看
words[j]有沒有符合條件 words[j]可能在words[i]不只出現過一次。所以我們需要找出所有可能。直到找出符合條件的或者沒有找到符合條件的。例如:timt(i),t(j),j在i出現了2次,而且有一個是符號條件的,也就是indices為3的t。
- 看看
class Solution {
public:
int minimumLengthEncoding(vector<string>& words){
set<string> unique(words.begin(),words.end()); //O(n)
vector<string> list;
for(auto word : unique) list.push_back(word); //O(n)
//sorting by word size
//O n log n
sort(list.begin(),list.end(),[&](string& a,string& b){
return a.length() > b.length();
});
vector<int> v(list.size(),0);
int res = 0;
//O n*n-1 = n^2
for(int i = 0;i<list.size();i++){
if(v[i]) continue;
for(int j = i+1;j<list.size();j++){
int index = list[i].find(list[j]);
if(index == -1) continue; //not found,go to next one
if(index != -1 && list[i].length() == index + list[j].length()){
v[j] = 1;
}else{
while((index = list[i].find(list[j],index)) != -1){
if(list[i].length() == index + list[j].length()) {
v[j] = 1;
break;
}
index ++;
}
}
}
res += list[i].length() + 1; //adding extra #
}
}
};